Preliminary combination
Warning
Before continuing, make sure that you have already initialize the file tree structure by following the instructions provided in the Initial file tree section of this documentation.
Warning
When combining a large number of images, and depending on the operating
system, users may get an error indicating OSError: [Errno 24] Too many
open files
You can easily check the maximum number of open files allowed in your operating system using
(emir) $ ulimit -Sn
This number can be easily increased employing
(emir) $ ulimit -n <number>
where <number> is the required number. Note that you need this number
to be at least twice the number of images to be combined (at some
particular steps during the image combination the pipeline requires to
access the intermediate images and the same number of mask files).
Assume you want to combine the following raw images obtained using a dithered pattern of 7 positions iterated twice (i.e., you have gathered a total of 14 images):
0001877553-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
0001877559-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
0001877565-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
0001877571-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
0001877577-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
0001877583-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
0001877589-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
0001877595-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
0001877601-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
0001877607-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
0001877613-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
0001877619-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
0001877625-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
0001877631-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
Those files (together with some additional files that you will need to follow this imaging example) are available as a compressed tgz file: pyemir_imaging_tutorial_v4.tgz.
The preliminary combination of these 14 images will be carried out in two steps:
Step 1: basic reduction of each individual image: bad-pixel masking, flatfielding and reprojection (the latter only since PyEmir version 0.17.0)
Step 2: actual combination of the images
Step 1: basic reduction of individual exposures
Move to the directory where you have deployed the initial file tree structure containing the basic PyEmir calibration files (see Initial file tree).
Decompress there the previously mentioned tgz file:
(emir) $ tar zxvf pyemir_imaging_tutorial_v4.tgz
...
...
(emir) $ rm pyemir_imaging_tutorial_v4.tgz
This action should have populated the file tree with the
14 scientific raw FITS (placed wihtin the data
subdirectory) and some additional auxiliary files:
(emir) $ tree
.
├── control.yaml
├── data
│ ├── 0001877553-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
│ ├── 0001877559-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
│ ├── 0001877565-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
│ ├── 0001877571-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
│ ├── 0001877577-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
│ ├── 0001877583-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
│ ├── 0001877589-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
│ ├── 0001877595-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
│ ├── 0001877601-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
│ ├── 0001877607-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
│ ├── 0001877613-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
│ ├── 0001877619-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
│ ├── 0001877625-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
│ ├── 0001877631-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
│ ├── master_bpm.fits
│ ├── master_dark_zeros.fits
│ ├── master_flat_ones.fits
│ ├── master_flat_spec.fits
│ ├── rect_wpoly_MOSlibrary_grism_H_filter_H.json
│ ├── rect_wpoly_MOSlibrary_grism_J_filter_J.json
│ ├── rect_wpoly_MOSlibrary_grism_K_filter_Ksp.json
│ ├── rect_wpoly_MOSlibrary_grism_LR_filter_HK.json
│ ├── rect_wpoly_MOSlibrary_grism_LR_filter_YJ.json
│ └── user_offsets.txt
├── dithered_ini.yaml
├── dithered_v0.yaml
├── dithered_v1.yaml
├── dithered_v2.yaml
├── dithered_v3.yaml
├── dithered_v4.yaml
└── dithered_v5.yaml
You can easily examine the header of the scientific FITS images using the
astropy utility fitsheader:
(emir) $ fitsheader data/0001877* \
-k nobsblck -k obsblock -k nimgobbl -k imgobbl \
-k nexp -k exp -k object -k exptime -k readmode \
-k filter -k grism -k date-obs -k ra -k dec -f > fitsheader_out.txt
The previous command generates a file fitsheader_out.txt with the contents
of some relevant FITS keywords extracted from the header of the images.
filename NOBSBLCK OBSBLOCK NIMGOBBL IMGOBBL NEXP EXP OBJECT EXPTIME READMODE FILTER GRISM DATE-OBS RA DEC
---------------------------------------------- -------- -------- -------- ------- ---- --- ------ -------- -------- ------ ----- ---------------------- ------------ -------------
data/0001877553-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits 18 1 7 1 1 1 TEST 29.99926 RAMP F1230 OPEN 2018-12-17T23:57:24.72 02:39:54.057 -01:34:33.537
data/0001877559-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits 18 1 7 2 1 1 TEST 29.99926 RAMP F1230 OPEN 2018-12-17T23:58:11.73 02:39:51.624 -01:35:09.313
data/0001877565-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits 18 1 7 3 1 1 TEST 29.99926 RAMP F1230 OPEN 2018-12-17T23:58:58.75 02:39:50.663 -01:34:19.381
data/0001877571-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits 18 1 7 4 1 1 TEST 29.99926 RAMP F1230 OPEN 2018-12-17T23:59:35.22 02:39:52.125 -01:34:01.301
data/0001877577-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits 18 1 7 5 1 1 TEST 29.99926 RAMP F1230 OPEN 2018-12-18T00:00:24.35 02:39:53.964 -01:35:08.879
data/0001877583-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits 18 1 7 6 1 1 TEST 29.99926 RAMP F1230 OPEN 2018-12-18T00:01:14.53 02:39:49.484 -01:34:51.913
data/0001877589-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits 18 1 7 7 1 1 TEST 29.99926 RAMP F1230 OPEN 2018-12-18T00:02:02.60 02:39:52.125 -01:34:41.302
data/0001877595-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits 18 2 7 1 1 1 TEST 29.99926 RAMP F1230 OPEN 2018-12-18T00:02:54.89 02:39:54.057 -01:34:33.537
data/0001877601-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits 18 2 7 2 1 1 TEST 29.99926 RAMP F1230 OPEN 2018-12-18T00:03:41.91 02:39:51.624 -01:35:09.313
data/0001877607-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits 18 2 7 3 1 1 TEST 29.99926 RAMP F1230 OPEN 2018-12-18T00:04:27.88 02:39:50.663 -01:34:19.381
data/0001877613-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits 18 2 7 4 1 1 TEST 29.99926 RAMP F1230 OPEN 2018-12-18T00:05:05.41 02:39:52.125 -01:34:01.350
data/0001877619-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits 18 2 7 5 1 1 TEST 29.99926 RAMP F1230 OPEN 2018-12-18T00:05:54.53 02:39:53.964 -01:35:08.879
data/0001877625-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits 18 2 7 6 1 1 TEST 29.99926 RAMP F1230 OPEN 2018-12-18T00:06:44.71 02:39:49.484 -01:34:51.913
data/0001877631-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits 18 2 7 7 1 1 TEST 29.99926 RAMP F1230 OPEN 2018-12-18T00:07:31.73 02:39:52.125 -01:34:41.302
Note that:
the keyword
OBSBLOCKgives the observing block number.the keyword
NIMGOBBLprovides the total number of images in each dithering pattern (7 in this case).IMGOBBLindicates the sequential number within each pattern. This number runs from 1 toNIMGOBBL.the keyword
NEXPgives the number of exposures taken at each position in the dithering pattern before moving to the next one. In this simple example this number is 1.the keyword
EXPprovides de sequential number at each position in the dithering pattern. This number runs from 1 toNEXP.
The first steps in the reduction process will be the bad-pixel mask, flatfielding, and image reprojection.
Note
Remember that the numina script is the interface with GTC pipelines.
In order to execute PyEmir recipes you should type something like:
(emir) $ numina run <observation_result_file.yaml> -r <requirements_file.yaml>
where <observation_result_file.yaml> is an observation result file in
YAML format, and <requirements_files.yaml> is a requirements file, also
in YAML format.
YAML is a human-readable data serialization language (for details see YAML Syntax)
The deployed file tree already contains the files required
to execute the initial reduction recipe needed in this case: the observation
result file dithered_ini.yaml and the requirements file control.yaml.
Let’s have a look to each of them separately.
The observation result file: dithered_ini.yaml
This is what we call an observation result file, which basically contains the reduction recipes to be applied and the images involved. Note that this particular file contains 14 blocks, one for each individual image.
Each block is separated by a line containing just three dashes (---):
Do not forget the separation line
---between blocks (otherwise the pipeline will not recognize where one block ends and the next one begins).This separation line must not appear after the last block.
The contents of this file is displayed below, highlighting the first block (first eight lines):
1id: _0001877553
2instrument: EMIR
3mode: STARE_IMAGE
4frames:
5 - 0001877553-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
6requirements:
7 reprojection_method: interp
8enabled: True
9---
10id: _0001877559
11instrument: EMIR
12mode: STARE_IMAGE
13frames:
14 - 0001877559-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
15requirements:
16 reprojection_method: interp
17enabled: True
18---
19id: _0001877565
20instrument: EMIR
21mode: STARE_IMAGE
22frames:
23 - 0001877565-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
24requirements:
25 reprojection_method: interp
26enabled: True
27---
28id: _0001877571
29instrument: EMIR
30mode: STARE_IMAGE
31frames:
32 - 0001877571-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
33requirements:
34 reprojection_method: interp
35enabled: True
36---
37id: _0001877577
38instrument: EMIR
39mode: STARE_IMAGE
40frames:
41 - 0001877577-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
42requirements:
43 reprojection_method: interp
44enabled: True
45---
46id: _0001877583
47instrument: EMIR
48mode: STARE_IMAGE
49frames:
50 - 0001877583-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
51requirements:
52 reprojection_method: interp
53enabled: True
54---
55id: _0001877589
56instrument: EMIR
57mode: STARE_IMAGE
58frames:
59 - 0001877589-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
60requirements:
61 reprojection_method: interp
62enabled: True
63---
64id: _0001877595
65instrument: EMIR
66mode: STARE_IMAGE
67frames:
68 - 0001877595-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
69requirements:
70 reprojection_method: interp
71enabled: True
72---
73id: _0001877601
74instrument: EMIR
75mode: STARE_IMAGE
76frames:
77 - 0001877601-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
78requirements:
79 reprojection_method: interp
80enabled: True
81---
82id: _0001877607
83instrument: EMIR
84mode: STARE_IMAGE
85frames:
86 - 0001877607-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
87requirements:
88 reprojection_method: interp
89enabled: True
90---
91id: _0001877613
92instrument: EMIR
93mode: STARE_IMAGE
94frames:
95 - 0001877613-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
96requirements:
97 reprojection_method: interp
98enabled: True
99---
100id: _0001877619
101instrument: EMIR
102mode: STARE_IMAGE
103frames:
104 - 0001877619-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
105requirements:
106 reprojection_method: interp
107enabled: True
108---
109id: _0001877625
110instrument: EMIR
111mode: STARE_IMAGE
112frames:
113 - 0001877625-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
114requirements:
115 reprojection_method: interp
116enabled: True
117---
118id: _0001877631
119instrument: EMIR
120mode: STARE_IMAGE
121frames:
122 - 0001877631-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
123requirements:
124 reprojection_method: interp
125enabled: True
The
idvalue is an arbitrary label that is employed to generate the name of two auxiliary subdirectories. In this example the reduction of the first block will generate two subdirectories namedobsid_0001877553_workandobsid_0001877553_results, where the intermediate results and the final results are going to be stored, respectively. Note that we have arbitrarily chosen the 10 digits of the unique running number assigned to each image obtained with the GTC to build the label.Not surprisingly, the key
instrumentis set to EMIR (do not forget that Numina is at present also employed to reduce MEGARA data, and hopefully, future GTC instruments).The key
modeindicates the identification of the reduction recipe (STARE_IMAGEin this example).The key
frameslists the images to be combined prior to the execution of the reduction recipe. In this case a single image has been obtained at each point of the dithering pattern before moving to the next location within the pattern. For that reason a single image appears in each block.The key
requirementsis employed to pass additional parameters to the reduction recipe. In this case, we are specifying the reprojection method to be employed in order to correct the images from distortions prior to their final combination. Since the reprojection is performed using the package reproject we can choose between the different resampling algorithms implemented in that package: valid values are:none(no reprojection is performed; this leads to bad results when combining dithered images, specially at the final image borders),interp(fastest reprojection method),adaptive, orexact(slowest). Please, have a look to the documentation in the** reproject package if you need additional information concerning the reprojetion methods. In this example we are using**interp, which provides good results and is fast.Warning
IMPORTANT: PyEmir users should try to use the slower
adaptiveor the slowestexactmethods, and compare the final combined images to check for the impact of the adopted method.The key
enabled: Trueindicates that this block is going to be reduced. As it is going to be shown later, the user can easily activate/deactivate the execution of particular reduction recipes (i.e. blocks in this file) just by modifying this flag.
Note
Since the generation of the file dithered_ini.yaml can be cumbersome,
specially
when the number of images is large, an auxiliary script has been
incorporated in PyEmir in order to help in its generation.
In particular, the file used in this example can be easily created using a few simple commands:
(emir) $ cd data/
(emir) $ ls 0001877*fits > list_images.txt
(emir) $ cd ..
(emir) $ pyemir-generate_yaml_for_dithered_image \
data/list_images.txt --step 0 --repeat 1 \
--reprojection interp \
--outfile dithered_ini.yaml
Note that a temporary file list_images.txt is created with a list of the
the individual exposures. The script
pyemir-generate_yaml_for_dithered_image reads that file and generates
the observation result file dithered_ini.yaml.
The parameter --step 0
indicates that the reduction recipe to be used here is STARE_IMAGE,
which corresponds to the preliminary image reduction.
The parameter --repeat 1 indicates that there is only a single exposure
at each telescope pointing within the dithering pattern. In a general case
this number can be greater than one (check the NEXP keyword in the FITS
header of the images; this is one of the keywords included in the file
fitsheader_out.txt generated above).
The reprojection method is also indicated by --reprojection interp,
where the valid options are none, interp, adaptive or exact.
The requirements file: control.yaml
This is the requirements file, containing the expected name of generic calibration files. You do not need to modify anything here.
1version: 1
2products:
3 EMIR:
4 225fcaf2-7f6f-49cc-972a-70fd0aee8e96: # original EMIR detector
5 - {id: 2, type: 'MasterBadPixelMask', tags: {}, content: 'master_bpm.fits'}
6 - {id: 3, type: 'MasterDark', tags: {}, content: 'master_dark_zeros.fits'}
7 - {id: 4, type: 'MasterIntensityFlat', tags: {}, content: 'master_flat_spec.fits'}
8 - {id: 5, type: 'MasterSpectralFlat', tags: {}, content: 'master_flat_spec.fits'}
9 - {id: 11, type: 'MasterRectWave', tags: {grism: J, filter: J}, content: 'rect_wpoly_MOSlibrary_grism_J_filter_J.json'}
10 - {id: 12, type: 'MasterRectWave', tags: {grism: H, filter: H}, content: 'rect_wpoly_MOSlibrary_grism_H_filter_H.json'}
11 - {id: 13, type: 'MasterRectWave', tags: {grism: K, filter: Ksp}, content: 'rect_wpoly_MOSlibrary_grism_K_filter_Ksp.json'}
12 - {id: 14, type: 'MasterRectWave', tags: {grism: LR, filter: YJ}, content: 'rect_wpoly_MOSlibrary_grism_LR_filter_YJ.json'}
13 - {id: 15, type: 'MasterRectWave', tags: {grism: LR, filter: HK}, content: 'rect_wpoly_MOSlibrary_grism_LR_filter_HK.json'}
14 - {id: 21, type: 'RefinedBoundaryModelParam', tags: {grism: J, filter: J}, content: 'final_multislit_bound_param_grism_J_filter_J.json'}
15 - {id: 22, type: 'RefinedBoundaryModelParam', tags: {grism: H, filter: H}, content: 'final_multislit_bound_param_grism_H_filter_H.json'}
16 - {id: 23, type: 'RefinedBoundaryModelParam', tags: {grism: K, filter: Ksp}, content: 'final_multislit_bound_param_grism_K_filter_Ksp.json'}
17 - {id: 24, type: 'RefinedBoundaryModelParam', tags: {grism: LR, filter: YJ}, content: 'final_multislit_bound_param_grism_LR_filter_YJ.json'}
18 - {id: 25, type: 'RefinedBoundaryModelParam', tags: {grism: LR, filter: HK}, content: 'final_multislit_bound_param_grism_LR_filter_HK.json'}
19 443fc0d1-e09a-48cc-a0fd-02be6f399da2: # H2RG detector
20 - {id: 2, type: 'MasterBadPixelMask', tags: {}, content: 'master_bpm_zeros.fits'}
21 - {id: 3, type: 'MasterDark', tags: {}, content: 'master_dark_zeros.fits'}
22 - {id: 4, type: 'MasterIntensityFlat', tags: {}, content: 'master_flat_spec_H2RG.fits'}
23 - {id: 5, type: 'MasterSpectralFlat', tags: {}, content: 'master_flat_spec_H2RG.fits'}
24 - {id: 11, type: 'MasterRectWave', tags: {grism: J, filter: J}, content: 'rect_wpoly_MOSlibrary_grism_J_filter_J.json'}
25 - {id: 12, type: 'MasterRectWave', tags: {grism: H, filter: H}, content: 'rect_wpoly_MOSlibrary_grism_H_filter_H.json'}
26 - {id: 13, type: 'MasterRectWave', tags: {grism: K, filter: Ksp}, content: 'rect_wpoly_MOSlibrary_grism_K_filter_Ksp.json'}
27 - {id: 14, type: 'MasterRectWave', tags: {grism: LR, filter: YJ}, content: 'rect_wpoly_MOSlibrary_grism_LR_filter_YJ.json'}
28 - {id: 15, type: 'MasterRectWave', tags: {grism: LR, filter: HK}, content: 'rect_wpoly_MOSlibrary_grism_LR_filter_HK.json'}
29 - {id: 21, type: 'RefinedBoundaryModelParam', tags: {grism: J, filter: J}, content: 'final_multislit_bound_param_grism_J_filter_J.json'}
30 - {id: 22, type: 'RefinedBoundaryModelParam', tags: {grism: H, filter: H}, content: 'final_multislit_bound_param_grism_H_filter_H.json'}
31 - {id: 23, type: 'RefinedBoundaryModelParam', tags: {grism: K, filter: Ksp}, content: 'final_multislit_bound_param_grism_K_filter_Ksp.json'}
32 - {id: 24, type: 'RefinedBoundaryModelParam', tags: {grism: LR, filter: YJ}, content: 'final_multislit_bound_param_grism_LR_filter_YJ.json'}
33 - {id: 25, type: 'RefinedBoundaryModelParam', tags: {grism: LR, filter: HK}, content: 'final_multislit_bound_param_grism_LR_filter_HK.json'}
34requirements:
35 EMIR:
36 225fcaf2-7f6f-49cc-972a-70fd0aee8e96: # original EMIR detector
37 default:
38 FULL_DITHERED_IMAGE:
39 - {name: 'x_offsets', tags: {}, content: 'ref_object_pos.txt'}
40 443fc0d1-e09a-48cc-a0fd-02be6f399da2: # H2RG detector
41 default:
42 FULL_DITHERED_IMAGE:
43 - {name: 'x_offsets', tags: {}, content: 'ref_object_pos.txt'}
Starting from March 2024, the format of this file has been updated to include calibrations for both the original EMIR detector and the subsequent replacement, the H2RG detector.
Numina execution
You are ready to execute the reduction recipe indicated in the file
dithered_ini.yaml (in this case the reduccion recipe named
STARE_IMAGE):
(emir) $ numina run dithered_ini.yaml -r control.yaml
...
...
After the execution of the previous command line, two subdirectories for each block should have appeared:
(emir) $ ls
control.yaml obsid_0001877565_results/ obsid_0001877601_work/
data/ obsid_0001877565_work/ obsid_0001877607_results/
dithered_ini.yaml obsid_0001877571_results/ obsid_0001877607_work/
dithered_v0.yaml obsid_0001877571_work/ obsid_0001877613_results/
dithered_v1.yaml obsid_0001877577_results/ obsid_0001877613_work/
dithered_v2.yaml obsid_0001877577_work/ obsid_0001877619_results/
dithered_v3.yaml obsid_0001877583_results/ obsid_0001877619_work/
dithered_v4.yaml obsid_0001877583_work/ obsid_0001877625_results/
dithered_v5.yaml obsid_0001877589_results/ obsid_0001877625_work/
obsid_0001877553_results/ obsid_0001877589_work/ obsid_0001877631_results/
obsid_0001877553_work/ obsid_0001877595_results/ obsid_0001877631_work/
obsid_0001877559_results/ obsid_0001877595_work/
obsid_0001877559_work/ obsid_0001877601_results/
The work subdirectories
All the relevant images (scientific and calibrations) involved in the reduction
of a particular block of the observation result file are copied into the
work subdirectories in order to preserve the original files.
In particular, for the first block:
(emir) $ tree obsid_0001877553_work/
obsid_0001877553_work/
├── 0001877553-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
├── index.pkl
├── mask_bpm.fits
├── master_dark_zeros.fits
└── master_flatframe.fits
When disk space is an issue, it is possible to execute numina indicating that
links (instead of actual copies of the original raw files) must be placed in
the work subdirectory. This behaviour is set using the parameter
--link-files:
(emir) $ numina run dithered_ini.yaml --link-files -r control.yaml
...
...
(emir) $ tree obsid_0001877553_work/
obsid_0001877553_work/
├── 0001877553-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits -> /Users/cardiel/w/GTC/emir/work/z_tutorials_201907/x/data/0001877553-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
├── index.pkl
├── master_bpm.fits -> /Users/cardiel/w/GTC/emir/work/z_tutorials_201907/x/data/master_bpm.fits
├── master_dark_zeros.fits -> /Users/cardiel/w/GTC/emir/work/z_tutorials_201907/x/data/master_dark_zeros.fits
└── master_flat_spec.fits -> /Users/cardiel/w/GTC/emir/work/z_tutorials_201907/x/data/master_flat_spec.fits
The results subdirectories
These subdirectories store the result of the execution of the reduction recipes. In particular, for the first block:
$ tree obsid_0001877553_results/
obsid_0001877553_results/
├── processing.log
├── reduced_image.fits
├── result.json
└── task.json
Note that although all the reduced images receive the same name in all these
results subdirectories (for this reduction recipe reduced_image.fits),
there is no confusion because the subdirectory name contains a unique label for
each block in the observation result file.
Step 2: image combination
After the basic reduction performed in step 1, we can proceed with the
combination of the images. For that purpose a different reduction recipe must
be employed: FULL_DITHERED_IMAGE.
This task is carried out using a new
observation result file: dithered_v0.yaml: the first 125 lines of this new
file are the same as the content of the the previous file
dithered_ini.yaml, but setting enabled: False in each of the 14 blocks.
This flag indicates that the execution of the recipe STARE_IMAGE is no
longer necessary in any of the 14 blocks. Note however that these blocks must
explicitly appear in the observation result file, even though they imply no
actual reduction, because they define the location of the previously reduced
images.
The new observation result file dithered_v0.yaml contains a new block at
the end (see lines 127-149 below), that is responsible of the execution of the
combination of the previously reduced images:
1id: _0001877553
2instrument: EMIR
3mode: STARE_IMAGE
4frames:
5 - 0001877553-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
6requirements:
7 reprojection_method: interp
8enabled: False
9---
10id: _0001877559
11instrument: EMIR
12mode: STARE_IMAGE
13frames:
14 - 0001877559-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
15requirements:
16 reprojection_method: interp
17enabled: False
18---
19id: _0001877565
20instrument: EMIR
21mode: STARE_IMAGE
22frames:
23 - 0001877565-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
24requirements:
25 reprojection_method: interp
26enabled: False
27---
28id: _0001877571
29instrument: EMIR
30mode: STARE_IMAGE
31frames:
32 - 0001877571-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
33requirements:
34 reprojection_method: interp
35enabled: False
36---
37id: _0001877577
38instrument: EMIR
39mode: STARE_IMAGE
40frames:
41 - 0001877577-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
42requirements:
43 reprojection_method: interp
44enabled: False
45---
46id: _0001877583
47instrument: EMIR
48mode: STARE_IMAGE
49frames:
50 - 0001877583-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
51requirements:
52 reprojection_method: interp
53enabled: False
54---
55id: _0001877589
56instrument: EMIR
57mode: STARE_IMAGE
58frames:
59 - 0001877589-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
60requirements:
61 reprojection_method: interp
62enabled: False
63---
64id: _0001877595
65instrument: EMIR
66mode: STARE_IMAGE
67frames:
68 - 0001877595-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
69requirements:
70 reprojection_method: interp
71enabled: False
72---
73id: _0001877601
74instrument: EMIR
75mode: STARE_IMAGE
76frames:
77 - 0001877601-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
78requirements:
79 reprojection_method: interp
80enabled: False
81---
82id: _0001877607
83instrument: EMIR
84mode: STARE_IMAGE
85frames:
86 - 0001877607-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
87requirements:
88 reprojection_method: interp
89enabled: False
90---
91id: _0001877613
92instrument: EMIR
93mode: STARE_IMAGE
94frames:
95 - 0001877613-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
96requirements:
97 reprojection_method: interp
98enabled: False
99---
100id: _0001877619
101instrument: EMIR
102mode: STARE_IMAGE
103frames:
104 - 0001877619-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
105requirements:
106 reprojection_method: interp
107enabled: False
108---
109id: _0001877625
110instrument: EMIR
111mode: STARE_IMAGE
112frames:
113 - 0001877625-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
114requirements:
115 reprojection_method: interp
116enabled: False
117---
118id: _0001877631
119instrument: EMIR
120mode: STARE_IMAGE
121frames:
122 - 0001877631-20181217-EMIR-STARE_IMAGE.fits
123requirements:
124 reprojection_method: interp
125enabled: False
126---
127id: _combined_v0
128instrument: EMIR
129mode: FULL_DITHERED_IMAGE
130children:
131 - _0001877553
132 - _0001877559
133 - _0001877565
134 - _0001877571
135 - _0001877577
136 - _0001877583
137 - _0001877589
138 - _0001877595
139 - _0001877601
140 - _0001877607
141 - _0001877613
142 - _0001877619
143 - _0001877625
144 - _0001877631
145requirements:
146 iterations: 0
147 sky_images: 0
148 refine_offsets: False
149enabled: True
The new block (lines 127-149) indicates that the reduction recipe
FULL_DITHERED_IMAGE must be executed using as input the results of the
previous blocks. In particular, the id's of the initial 14 blocks are given
under the children: keyword (lines 131 to 144).
In addition, a few parameters (which will be modified later) are set to some default values in this initial combination:
iterations: 0: this parameter indicates whether an object mask is employed or not. A value of0means that no object mask is computed. Note that an object mask allows a better sky background determination since bright objects are removed prior to the sky signal estimation. When this parameter is greater than zero, an object mask is created by performing a SEXtractor-like object search in the resulting image at the end of the previous iteration.sky_images: 0: number of images employed to determine the sky background of each pixel. Setting this parameter to0indicates that the sky background is simply computed as the median value in the same image in which the pixel background is being estimated. Using a value larger than zero sets the number of closest images (in time) where the signal of a particular pixel is averaged (for example, a value of6will tipically mean that the sky background will be estimated using 3 images acquired before and 3 images acquired after the current one; note that at the beginning and at the end of a given observation sequence, the closest nearby images correspond to exposures obtained only after or only before the current one, respectively).refine_offsets: False: this flag indicates whether the offsets between images must be refined using cross-correlation of subimages around the brightest objects.
As it will be explained later, the use of these parameters can help to obtain better results. So far we are only interested in showing a fast way to generate a combined image.
Note
The file dithered_v0.yaml can also be automatically generated using
the same script previously mentioned in step 1:
(emir) $ pyemir-generate_yaml_for_dithered_image \
data/list_images.txt --step 1 --repeat 1 \
--reprojection interp \
--obsid_combined combined_v0 \
--outfile dithered_v0.yaml
Note that here we are using --step 1 instead of --step 0. In
addition, a new parameter --obsid_combined combined_v0 has also been
employed in order to set the id of the block responsible for the
execution of the combination recipe.
Do not miss the --repeat <NEXP> parameter (in this example
NEXP=1).
The combination of the images is finally performed using numina:
(emir) $ numina run dithered_v0.yaml --link-files -r control.yaml
The previous execution also generates two auxiliary subdirectories work and
results. The resulting combined image can be found in
obsid_combined_v0_result/reduced_image.fits:
(emir) $ tree obsid_combined_v0_results/
obsid_combined_v0_results/
├── processing.log
├── reduced_image.fits
├── result.json
└── task.json
You can display the image using ds9, using numina-ximshow (the display
tool shipped with numina based on matplotlib), or with any other tool:
(emir) $ numina-ximshow obsid_combined_v0_results/reduced_image.fits
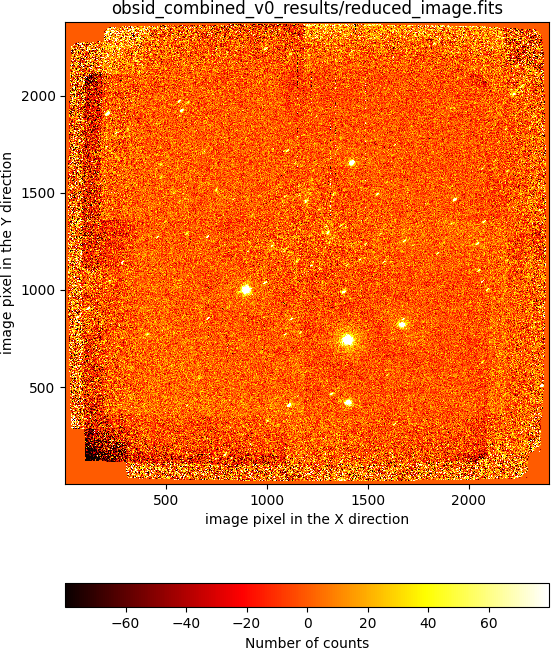
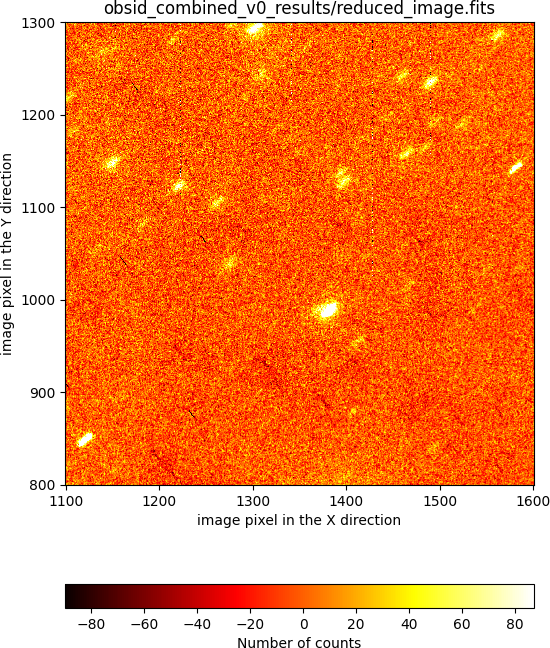
It is clear that this combined image is far from perfect. In particular, there are inhomogeneities in the background level, which are easier to see at the image borders. In addition, the objects appear elongated, which indicates that the offsets between individual exposures, determined from the WCS header information, are not suficiently precise. The zoomed region shown in the next image reveals that the problem is not negligible:
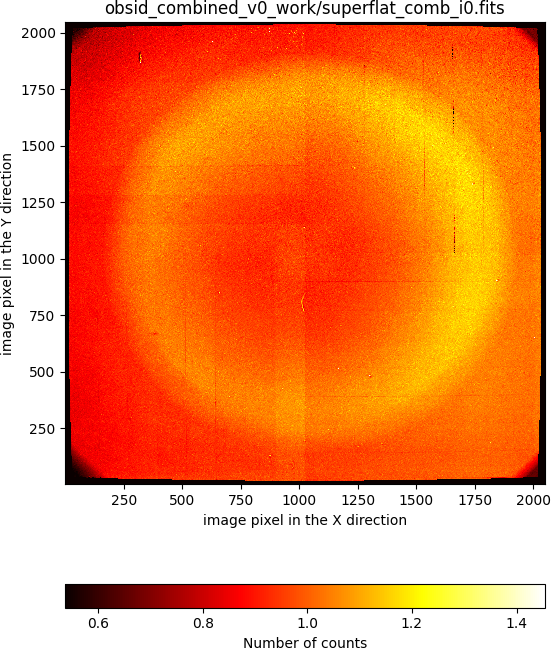
In addition, the superflatfield computed when combining the individual
exposures does exhibit a doughnut-like shape that must be taken account
(something that we have not yet done). In particular, the image
obsid_combined_v0_work/superflat_comb_i0.fits has the following aspect:
In the next section we are showing several alternatives to handle the previous issues and improve the image combination.